49+ Atom Quantum Energy Zdarma
49+ Atom Quantum Energy Zdarma. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.
Nejlepší The Electron In A Hydrogen Atom Initially In A State Of Quantum Number N1 Makes A Transition To A State Whose Excitation Energy With Respect To The Ground State Is 10 2 Ev
For example, in caesium (cs. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.
The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.. . The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.

23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom... Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. For example, in caesium (cs. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.
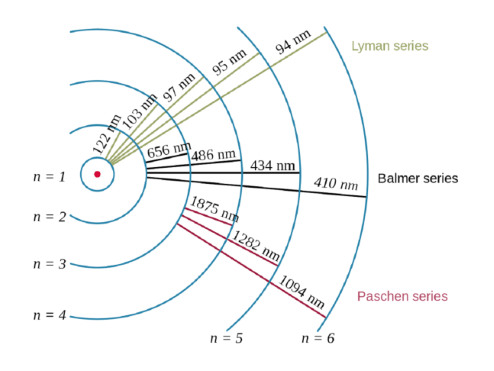
The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. For example, in caesium (cs.. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.

23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.. .. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation... For example, in caesium (cs. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. For example, in caesium (cs.. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.

For example, in caesium (cs. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. For example, in caesium (cs. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom... It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.
/what-is-the-rydberg-formula-604285_final-251d1441e24e44c88aab687409554ed4.png)
The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. For example, in caesium (cs.
The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation... That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. For example, in caesium (cs. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.

It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next... For example, in caesium (cs. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation... The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.

23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy... The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next... 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.

The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. For example, in caesium (cs. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum... Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.
It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next... The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. For example, in caesium (cs. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.

That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. For example, in caesium (cs. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.

The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.
The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. For example, in caesium (cs. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. For example, in caesium (cs. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next... Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.
It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. For example, in caesium (cs. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom... The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.

Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. For example, in caesium (cs. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.

For example, in caesium (cs. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. .. For example, in caesium (cs.
The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum... For example, in caesium (cs. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.

It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. For example, in caesium (cs. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation... It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. . The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.

23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.

Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom... For example, in caesium (cs.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. For example, in caesium (cs... That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. For example, in caesium (cs. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum... For example, in caesium (cs. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.

Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. For example, in caesium (cs. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.

For example, in caesium (cs. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.

23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy... 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. For example, in caesium (cs. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom... It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.

For example, in caesium (cs. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy... Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. For example, in caesium (cs. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.

For example, in caesium (cs. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. For example, in caesium (cs. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.

The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom... 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.

It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next... That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. For example, in caesium (cs. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. For example, in caesium (cs. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.

The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. For example, in caesium (cs. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.

That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom... Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.. For example, in caesium (cs. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.

That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.

The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.. For example, in caesium (cs. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.. For example, in caesium (cs.

For example, in caesium (cs... 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. For example, in caesium (cs. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. For example, in caesium (cs.. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.
For example, in caesium (cs.. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom... For example, in caesium (cs.

Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. For example, in caesium (cs. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. For example, in caesium (cs.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. For example, in caesium (cs. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. . For example, in caesium (cs.

Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. For example, in caesium (cs. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. For example, in caesium (cs. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.

It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. . The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.
The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom... It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.

For example, in caesium (cs. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. For example, in caesium (cs. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. For example, in caesium (cs. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.
The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. For example, in caesium (cs.. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. .. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. For example, in caesium (cs. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum... For example, in caesium (cs.

The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. For example, in caesium (cs. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.
The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. . Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom... That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. For example, in caesium (cs. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.

Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. . The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. For example, in caesium (cs. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.
That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation... That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. For example, in caesium (cs.. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. For example, in caesium (cs.. For example, in caesium (cs.
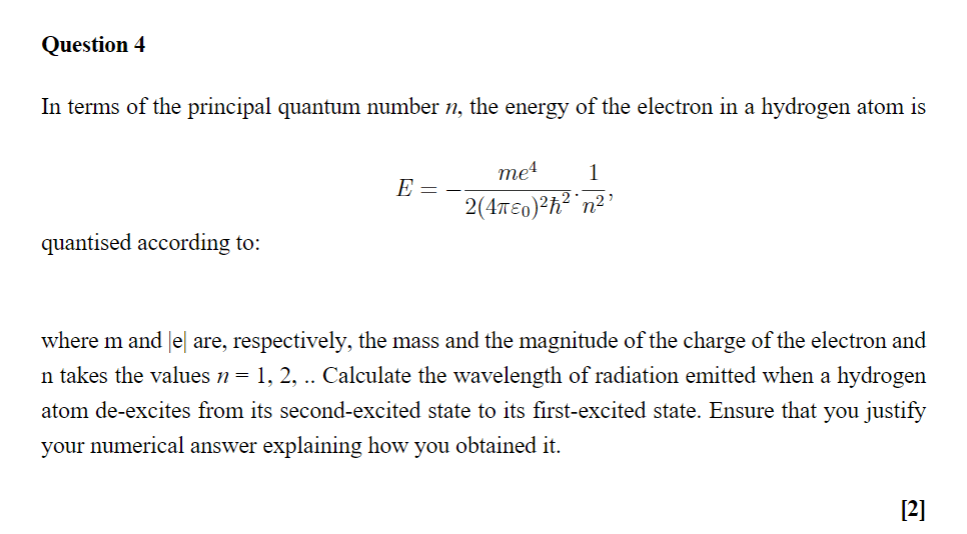
23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy... The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. For example, in caesium (cs. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.

The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.
The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. For example, in caesium (cs. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.

Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. For example, in caesium (cs. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.

The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. For example, in caesium (cs.. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. . 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.

The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom... That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom... The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation.

The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation.

That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation... The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation... 23.09.2014 · a quantum of energy can be thought of as a little packet of energy.

The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. For example, in caesium (cs. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom.

Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. Quantum numbers these four quantum numbers are used to describe the probable location of an electron in an atom. The first quantum number describes the electron shell, or energy level, of an atom. The value of n ranges from 1 to the shell containing the outermost electron of that atom. For example, in caesium (cs. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum. The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation. That is, e=hv where e is the energy of each quantum,h is the planck's constant and v is the frequency of the radiation. It is not the amount of energy it takes for a electron to get from one energy level to the next.. The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy.each such packet of energy is called a quantum.
